EV's and their Variants explained 🚗⚡️🔋 #ElectricVehicles #Cars #Technology #EVs #Automobiles
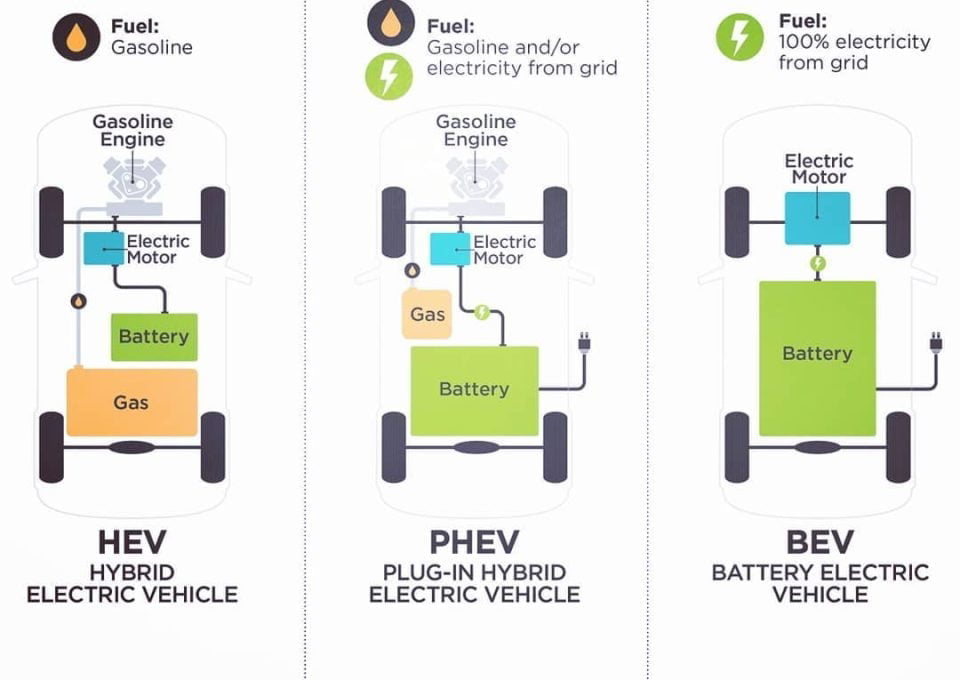
1. HEV (Hybrid Electric Vehicle) Powertrain: Uses both a gasoline engine and an electric motor. Battery: Small battery charged through regenerative braking and the gasoline engine. Fuel Source: Gasoline-only (battery assists but does not provide independent propulsion). Charging: Cannot be plugged in; relies on the engine and regenerative braking for recharging. Operation: Runs primarily on the gasoline engine. The electric motor assists in improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. At low speeds or short distances, it may run purely on the electric motor, but not for long. Example Models: ✅️Toyota Prius (HEV), Honda Accord Hybrid (Global) ✅️ Honda City Hybrid eHev , Toyota Innova Hycross 2. PHEV (Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle) Powertrain: Uses both a gasoline engine and a larger electric motor than HEVs. Battery: Larger battery than HEVs, allowing for independent electric-only driving. Fuel Source: Uses both gasoline and electricity. Can run on electric...

